Ethernet Essentials
By far the most common Local Area Network (LAN) technology that any modern network engineer is going to see is Ethernet. Ethernet has been around for over 30 years now in different variations and continues to be the technology that evolves to the needs of the network. Ethernet has even been modified for use in larger scale Wide Area Network (WAN) deployments. This article takes a look at what Ethernet is, what is contained within the Ethernet frame structure, common Ethernet LAN devices and discusses the different Ethernet interface variations.
The Ethernet Frame
Of all the different frame and packet formats that will be learned over the career of a typical network engineer, the Ethernet frame is one of the simplest. As shown in Figure 1, there are only five different fields that are mostly self-explanatory. They are as follows:
- Destination MAC Address—This is the MAC address where the frame is addressed to. Keep in mind that this is the destination address on the local network and may not be the final destination for the traffic being sent. (i.e. the default gateway would be a common local destination, but is not the final destination for most traffic)
- Source MAC Address—This is the MAC address where the frame was originated.
- Type (or EtherType) —This field is used to indicate the protocol type that is encapsulated within the frame. (The most common is 0x0800 IP).
- Data—This is where the frame data/payload is held; the size is dependent on the traffic size and the configuration on the source.
- CRC—The cyclic redundancy check (CRC) is a hash that is calculated at both the source and destination; if the destination CRC is not the same as what is contained with the frame then the frame has been corrupted in transit.
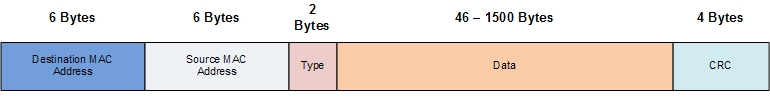
Figure 1 Ethernet Frame (Ethernet_II)
Ethernet Devices
There are a number of different Ethernet devices that exists on modern networks, the most common being switches and routers. However, there are also a number of different Ethernet devices that can exist on older networks; being familiar with these is also important. The following lists the common Ethernet devices that have been deployed in the last 20 years (For more detail, take a look at the LAN Device Review article):
- Hub—One of the most basic Ethernet devices; a hub is essentially a multiport repeater that connects and relays the data from all connected devices. All devices that are connected to a hub share the available bandwidth and see ALL traffic from each other.
- Bridge—A bridge was traditionally used to connect together different networks. The bridge offered the ability for a part of the network to be isolated at the physical layer but still allowed direct communications through at the data link layer. Devices on either side of the bridge could communicate but only through the bridge, this created the ability to split the collision domain. A collision occurs on a shared Ethernet segment when two devices attempt to communicate at the same time; this is covered further in the Access Methods section.
- Switch— A switch is essentially a multiport bridge, each switch port is its own shared domain. Typically, each switchport is only connected to a single device which prevents situations where collisions can occur.
- Router—A router is used to add another level of separation to the network. Even when in a switched network environment, devices are able to speak to each other directly at the data link layer. This is an advantage and a disadvantage, this means that any local device is able to send a Layer 2 broadcast that will be received and processed by ALL other devices on the local network. This is one of the main reasons why networks that have more than a couple of devices need to have routers added. Routers provide the ability to both separate networks into different broadcast domains and offer the ability to control traffic going between different Layer 2 networks.
Access Methods
On shared media networks, a method must exist that enables multiple devices to communicate over the same network. With wired Ethernet, the mechanism used is Carrier Sense Multiple Access—Collision Detect (CSMA/CD). The CSMA/CD method allows multiple devices to exist as well as send and receive traffic on the same shared network; each of the devices is tasked with listening to the traffic on the network and only attempting to send data when the network is idle. Devices also require a mechanism to be defined that is used when more than one station attempts to use the network at the same time; this is referred to as a collision. With CSMA/CD, a collision is detected and a jam message is sent to notify all devices that a collision has occurred, at this point each of the stations stop attempting to transmit and waits a random amount of time before attempting to transmit again.
Wireless Ethernet networks use a slightly different access control mechanism called Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Avoidance (CSMA/CA). Since wireless radios are not able to both send and receive at the same time collision detection is not possible. Some operations are similar to CSMA/CD, a device listens to the network and waits until it detects that the network is idle, when this is detected the device then transmits. Often the CSMA/CA mechanism is combined with a Ready to Send/Clear to Send (RTS/CTS) mechanism. When using RTS/CTS, a device first sends a RTS message; if the device does not receive a CTS message in a specified amount of time then the device will wait a random amount of time and send another RTS message. When using this mechanism, no traffic is sent until a CTS message has been received; this avoids the possibility of collisions on the network.
It is important to note that in fully switched networks where each switch port is only connected to a single device, the access methods detailed above are not required as communications can happen in full duplex over separate physical pairs.
Ethernet Interface Standards
There are certainly a number of different interface standards that exist for Ethernet; Table 1 shows the common standards that are deployed and where they are defined within the standard.
Table 1: Ethernet Interface Standards
|
IEEE 802.3 |
10-Base-5 (Thick-net) |
|
IEEE 802.3a |
10-Base-2 (Thin-net) |
|
IEEE 802.3i |
10-Base-T |
|
IEEE 802.3u |
100-Base-TX |
|
IEEE 802.3z |
1000-Base-X (Gigabit Ethernet over Fiber) |
|
IEEE 802.3ab |
1000-Base-T (Gigabit Ethernet over Copper) |
|
IEEE 802.3ae |
10-GBase-SR, 10-GBase-LR, 10-GBase-ER, 10-GBase-SW, 10-GBase-LW, 10-GBase-EW |
|
IEEE 802.3an |
10-GBase-T |
Summary
Ethernet networks have been a mainstay in local area networks for the last 30 years and will most likely continue this way for the next few decades. Being familiar with Ethernet, how it operates and the different Ethernet (IEEE 802.3) standards make the job of a network engineer much easier. Hopefully, this article has been able to give the reader an idea of what Ethernet is, the devices that use it, and the basics of how it operates.