- Isolation Response
- Split-Brain
- Isolation Detection
- Failure Detection Time
Isolation Detection
We have explained what the options are to respond to an isolation event. However we have not extensively discussed how isolation is detected. This is one of the key mechanisms of HA. Isolate detection is a mechanism which takes place on the host that is isolated. The remaining, non-isolated, hosts don’t know if that host has failed completely or if it is isolated from the network, they only know it is unavailable.
The mechanism is fairly straightforward though and works as earlier explained with heartbeats. When a node receives no heartbeats from any of the other nodes for 13 seconds (default setting) HA will ping the “isolation address”. Remember primary nodes send heartbeats to primaries and secondaries, secondary nodes send heartbeats only to primaries.
The isolation address is the gateway specified for the Service Console network (or management network on ESXi), but there is a possibility to specify one or multiple additional isolation addresses with an advanced setting. This advanced setting is called “das.isolationaddress” and could be used to reduce the chances of having a false positive. We recommend to set at least one additional isolation address.
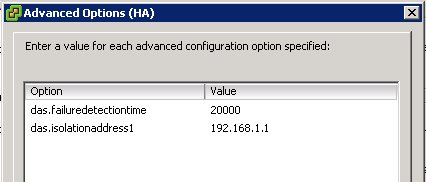
Figure 4: das.isolationaddress
When isolation has been confirmed, meaning no heartbeats have been received and HA was unable to ping any of the isolation addresses, HA will execute the isolation response. This could be any of the above described options, power down, shut down or leave powered on.
If only one heartbeat is received or just a single isolation address can be pinged the isolation response will not be triggered, which is exactly what you want.
Selecting an Additional Isolation Address
A question asked by many people is which address should be specified for this additional isolation verification. We generally recommend an isolation address closest to the hosts to avoid too many network hops. In many cases the most logical choice is the physical switch to which the host is directly connected, another usual suspect would be a router or any other reliable and pingable device.